Blood Glucose Monitoring
Oyster Point Family Practice is pleased to offer blood glucose monitoring to our patients with diabetes or pre-diabetic markers. Everyone with diabetes should test their blood sugar, or glucose, levels regularly. Knowing your blood sugar levels allows you to alter your diabetes management strategy if your levels aren't near your target blood sugar.
Also, regular testing of your blood sugar can help reduce your risk of having long-term complications from diabetes. Based on studies of people with type 1 diabetes (Diabetes Control and Complications Trial [DCCT]) and type 2 diabetes (United Kingdom Prevention of Diabetes [UKPDS]), maintaining near normal blood sugar and HbA1c levels significantly reduces the risks of complications from diabetes.
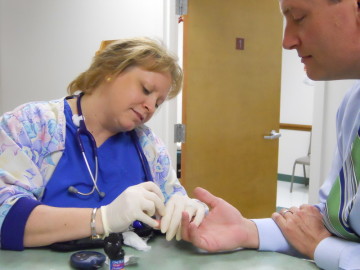
There are a few ways to test and track your blood glucose (sugar) levels. One of the tests is done by using glucometer (a device with the ability to test the amount of sugar in the blood). It is a simple procedure - the finger is pierced with a tiny needle and a drop of blood is placed on the testing paper which is then inserted into the monitor. After a few seconds, a number will appear on the screen - this is your blood sugar level. We perform this test on all our diabetic patients when they visit our office and on other patients who present the symptoms of diabetes.
Another method of testing for diabetes and the amount of glucose in the blood is through a Glucose Tolerance Test or GTT. This test is done by having the patient fast after midnight and taking several blood sugar readings after the patient drinks a sugar-based testing drink. After the patient arrives at the office and before he drinks the glucose drink, his blood sugar will be tested in the manner outlined above. The patient then drinks the glucose drink and waits in the lobby for his next test. After 30 minutes, his blood sugar will be taken again and recorded. After another hour, it is taken again and then taken one more time three hours after the drink was ingested.
This test gives the physician a much clearer picture of whether or not a patient has diabetes or is in the pre-stages of diabetes and can still be treated to avert the acquisition of the disease.
Another test that can be performed to monitor glucose is a urine test. This test measures the amount of ketones in the body. While ketones can be used to produce energy for the body, too many of them can cause a life-threatening condition called ketoacidosis in diabetic patients. It also measures the glucose to check if a patient has severe hyperglycemia which can lead to complications.
This test is very simple. A patient urinates into a cup and the urine is then tested with a machine that measures the glucose and ketones in the urine. Every diabetic patient seen in our office has this test at least once a year at their followup appointment.
For more information on diabetes treatment and symptoms, click here. You may also wish to visit the website of the American Diabetes Association.